Technology独自の技術
技術概要
Proprietary technology
-
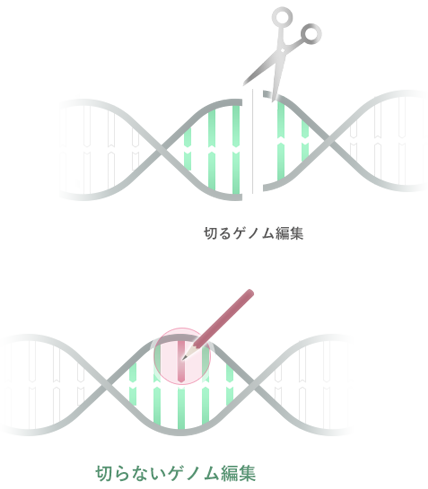
バイオパレットのコア技術は、DNAを切断しない新しいゲノム編集(切らないゲノム編集®)です。CRISPR/Cas9に代表される従来のゲノム編集がヌクレアーゼによるDNA二本鎖の切断を前提としているのに対して、切らないゲノム編集®は塩基の変換を誘導する酵素(塩基変換酵素)により点変異を導入する技術です。
より具体的には、CRISPRシステムのCas9タンパク質が有するヌクレアーゼ活性を不活性化し(dCas9またはnCas9)、塩基変換酵素と複合体を形成させることで、配列特異的にDNA上の特定領域に塩基変換酵素を作用させて点変異を導入するもので、この技術は一般的に塩基編集と呼ばれています。バイオパレットでは、塩基変換酵素の種類により、Target-AID®およびTarget-G®という2種類の塩基編集技術を有しています。Bio Palette’s core technology is a new type of genome editing that does not involve DNA cleavage (so-called, “Non-Cutting” genome editing). While conventional genome editing using techniques such as CRISPR/Cas9 requires the DNA double strand to be cleaved with nuclease, “Non-Cutting” genome editing introduces point mutations using enzymes that induce base conversion (base converting enzymes).
More specifically, by inactivating the nuclease activity of the Cas9 protein in the CRISPR system (dCas9 or nCas9) and forming a complex with a base converting enzyme, it introduces point mutations by causing base converting enzyme to act on a specific DNA region in a sequence-specific manner. This technology has become generally known as base editing. Bio Palette has two types of base editing technology, Target-AID® and Target-G®, each using a different type of base converting enzyme. -

-
Target-AID®
Target-AID®は、DNA上の標的部位にピンポイントかつ特定パターンの塩基置換を起こす技術です。
Target-AID®では、塩基変換酵素として脱アミノ化活性を有するシチジンデアミナーゼ(Activation-induced cytidine deaminase: AID)を使用します。シトシンは脱アミノ化されるとウラシルへ変換され、RNA塩基であるウラシルがDNA上ではチミンとして認識されることで、結果的にシトシンがチミンに変換されます。CRISPRシステムによって形成される標的領域の一本鎖DNAが露出した部分にのみAIDが作用するため、非常に特異的な範囲(5 bp以内)のシトシン(C)をチミン(T)に変換することができます。Target-AID® is a technology that causes base replacement in a specific pattern at a pinpointed target site in the DNA.
Target-AID® uses cytidine deaminase (activation-induced cytidine deaminase: AID), which has deamination activity, as a base converting enzyme. When cytosine is deaminated, it is converted to the RNA base uracil, which is recognized as thymine in DNA, and as a result, it is converted to thymine. Since AID acts only on the section of exposed single-strand DNA in the target region formed by the CRISPR system, it can convert cytosine (C) to thymine (T) within an extremely specific range (within 5 bp). -

-
Target-G®
Target-G®は、DNA上の一定範囲にランダムな塩基置換を起こす技術です。
Target-G®では、塩基変換酵素として脱塩基(塩基除去)反応を誘導するグリコシラーゼを使用します。脱塩基が生じた部分には任意の塩基が補充されるため、ランダムな塩基置換が起こります。グリコシラーゼの特性上、Target-G®は標的化した領域を中心として約1,000 bpの範囲に作用します。一定の領域にランダム変異を入れてバリエーション化することで、変異体ライブラリ作成や進化工学育種に利用できます。Target-G® is a technology that causes random base conversion within a certain range in the DNA.
Target-G® uses glycosylase, which induces an abasic (base excision) reaction, as a base converting enzyme. Since the parts where base excision occurs can be replenished with any base, random base conversion occurs. Because of the characteristics of glycosylase, Target-G® acts on ranges of approximately 1,000 bp around targeted regions. It is used for the creation of mutant libraries or for evolutionary engineering, by creating variation due to the introduction of random mutations within a certain region. -

Target-AID®とTarget-G®の比較
Comparison chart
|
コア技術 Core technology |
塩基変換酵素 Base converting enzyme |
作用領域 Region of action |
効果 Effect |
|---|---|---|---|
| Target-AID® |
デアミナーゼ
Deaminase |
5 bp以内の領域 Region within 5 bp |
特定パターンの塩基置換
Base conversion in a specific pattern |
| Target-G® |
グリコシラーゼ
Glycosylase |
1 kbp程度の領域 Region of around 1 kbp |
ランダムな塩基置換
Random base replacement |
|
コア技術 Core technology |
Target-AID® | Target-G® |
|---|---|---|
|
塩基変換酵素 Base converting enzyme |
デアミナーゼ
Deaminase |
グリコシラーゼ
Glycosylase |
|
作用領域 Region of action |
5 bp以内の領域 Region within 5 bp |
1 kbp程度の領域 Region of around 1 kbp |
|
効果 Effect |
特定パターンの塩基置換
Base conversion in a specific pattern |
ランダムな塩基置換
Random base replacement |
-
主なメリットと応用イメージ
Advantages and applications
切るゲノム編集であるCRISPR/Cas9は、DNA上の特定領域を標的化して遺伝子を編集するツールとして極めて革新的な技術です。CRISPR/Cas9の各種分野での産業応用が試みられる中で、技術の改善検討が世界中で進められ、より実用的な技術が誕生してきています。切らないゲノム編集®もCRISPR/Cas9を進歩させた技術です。
切らないゲノム編集®の特徴は、DNA二本鎖の切断に起因する制約や課題を回避することができる点にあります。CRISPR/Cas9, which is genome editing with cutting, is an extremely innovative technology providing a tool for editing genes in targeted specific regions of DNA. While the industrial application of CRISPR/Cas9 is being attempted in a range of fields, studies to improve the technology are being pursued around the world, leading to the birth of more practical technologies. “Non-Cutting” genome editing is one of these technologies developed from advancements based on CRISPR/Cas9. The special characteristic of “Non-Cutting” genome editing is that it can avoid the limitations and issues that arise from the cleavage of the DNA double strand.


-
- ・切断DNAの細胞による修復機構を利用して編集を行う「切るゲノム編集」の場合、一定の不確実性の下で編集結果が得られます(点変異、欠失、挿入などが入り混じった結果となる)。一方で、塩基編集は、基本的には点変異のみを生じ、精密性が非常に長けています。
- ・染色体切断が大きなストレスとなる細胞(細菌等)においても塩基編集を適用できます。細胞毒性が低いという点が塩基編集の特徴のひとつです。
- ・細胞毒性の低さと関連し、塩基編集では多箇所を同時に編集することができます。大腸菌を対象として同時に20箇所以上を標的化できることが実証されています。
- ・In the case of "Cutting” genome editing, which uses a cellular repair mechanism of cleaved DNA, editing results with some degree of uncertainty are expected (the results contain a mixture of changes including point mutations, deletions, and insertions).
- ・Base editing can also be used on cells (such as bacteria) on which chromosome cleavage would exert great stress. Low cytotoxicity is one of the characteristics of base editing.
- ・An ability of base editing relating to its low cytotoxicity is that multiple locations can be edited at once. It has been proven that in Escherichia coli, at least 20 locations can be targeted at once.
|
主なメリット
Main advantages of “Non-Cutting” |
応用イメージ Anticipated applications |
|---|---|
|
1
正確・精密に一塩基単位での編集ができる Accurate and precise editing can be performed, a single base at a time |
正確な遺伝子編集が求められるセラピューティクスや Application to fields such as therapeutics or drug discovery tools, which require accurate gene editing |
|
2
微生物を含む多様な生物種を対象にできる It can be used in a variety of biological species, including microorganisms |
切るゲノム編集の適用が困難であった生物種への Broadening of applications to microorganisms in which the use of genome editing with cutting is difficult (in particular, applications in cultivating microorganisms such as bacteria) |
|
3
多箇所の同時編集ができる Multiple locations can be edited at once |
多様な変異体の作製が求められる、機能性微生物や More efficient cultivation of functional microorganisms or useful crops that require production of a variety of mutant forms |
知財戦略
IP strategy
ゲノム編集技術を産業利用する上で重要となる特許は、少数の研究機関によって確保されています。世界のゲノム編集のスタンダードとなっているCRISPR/Cas9は、カリフォルニア大学バークレー校とブロード研究所(ハーバード大学とマサチューセッツ工科大学の研究機関)が基本的な特許を有しています。一方、デアミナーゼによる塩基編集についても、神戸大学とハーバード大学がそれぞれ独自に実証し、それぞれが基本的な知的財産を有しています。
The important patents for industrial use of genome editing technology have been acquired by a small number of research institutions. The basic patents for the world standard in genome editing, CRISPR/Cas9, are held by the University of California at Berkeley and the Broad Institute (a research institution of Harvard University and the Massachusetts Institute of Technology). On the other hand, base editing using deaminase has been demonstrated independently by Kobe University and Harvard University, and each has basic intellectual property for this technology.
ゲノム・塩基編集の戦略的パートナーシップ
Genome/Base Editing Strategic Partnership
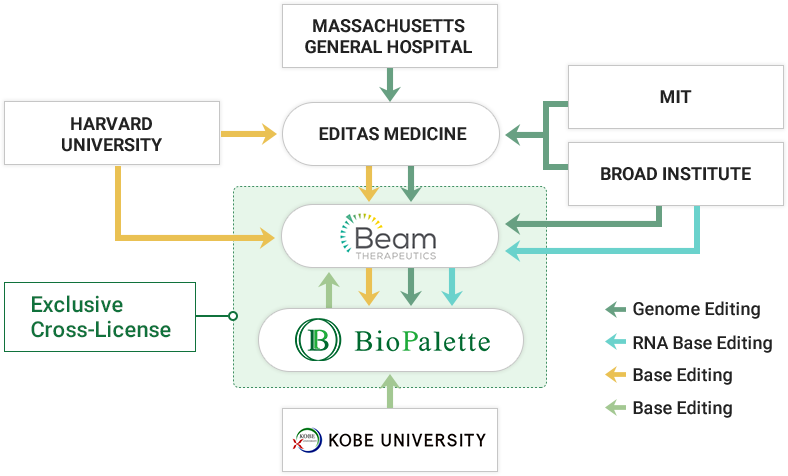
バイオパレットは神戸大学との密な連携のもと、神戸大学が特許出願済みのTarget-AID®、Target-G®およびその他の関連技術について、各国での権利化を進めています。また、各応用分野における新たな技術開発を神戸大学との連携のもと行っています。さらに、米国を中心とする有力機関との戦略的アライアンスによって、事業展開を見据えた上で知財ポートフォリオを拡充・構築しています。
戦略的アライアンスの一例が、Human Therapeutics分野においてハーバード大学の塩基編集の事業化を目指すBeam Therapeutics社と締結した独占的クロスライセンス契約です。Beam Therapeutics社は、ハーバード大学の他、ブロード研究所(MIT)、マサチューセッツ総合病院、Editas Medicineからゲノム編集関連技術の実施許諾を受けて、塩基編集の事業化に取り組んでいます。この契約によってバイオパレットは、Microbiome Therapeutics分野において、Beam Therapeutics社の有する知的財産を独占的に使用することができます。
Bio Palette is working in close coordination with Kobe University to secure rights in different countries for Target-AID®, Target-G® and other related technologies, for which Kobe University has made patent applications. We are also working in coordination with Kobe University on developing new technologies in applicable fields. In addition, we are broadening and constructing an intellectual property portfolio with a view to developing our business through strategic alliances with influential institutions, mainly in the US.
One example of our strategic alliances is an exclusive cross-licensing agreement with Beam Therapeutics, which aims to commercialize Harvard University’s base editing in the field of human therapeutics. In addition to Harvard University, Beam Therapeutics has also licensed related genome editing technology from Broad Institute (MIT), Massachusetts General Hospital and Editas Medicine, and is working on commercializing base editing. This agreement gives Bio Palette exclusive use of the intellectual property owned by Beam Therapeutics in the field of microbiome therapeutics in Asia.
論文情報
Article information
- Nishida K, Arazoe T, Yachie N, Banno S, Kakimoto M, Tabata M, Mochizuki M, Miyabe A, Araki M, Hara KY, Shimatani Z, Kondo A, Targeted nucleotide editing using hybrid prokaryotic and vertebrate adaptive immune systems. Science, 16 Sep 2016: Vol. 353, Issue 6305, aaf8729
- Shimatani Z, Kashojiya S, Takayama M, Terada R, Arazoe T, Ishii H, Teramura H, Yamamoto T, Komatsu H, Miura K, Ezura H, Nishida K, Ariizumi T, Kondo A, Targeted base editing in rice and tomato using a CRISPR-Cas9 cytidine deaminase fusion. Nature Biotechnology, volume 35, pages 441–443 (2017)
- Banno S, Nishida K, Arazoe T, Mitsunobu H, Kondo A, Deaminase-mediated multiplex genome editing in Escherichia coli. Nature Microbiology, volume 3, pages 423–429 (2018)
- Li A, Mitsunobu H, Yoshioka S, Suzuki T, Kondo A and Nishida K, Cytosine base editing systems with minimized off-target effect and molecular size. Nature Communications, volume 13, Article number: 4531(2022)
その他の分野への応用
Other fields of application
-
ヒト治療(ヒト細胞が対象)
Human Therapeutics
(Targeting human cells)精密かつ正確な遺伝子編集を実現する塩基編集(Target-AID®)は、ヒト治療の分野における応用が期待されています。塩基編集を利用すれば、遺伝子破壊のみならず、DNA断片の挿入を伴わない遺伝子修復が原理的に可能です。遺伝性疾患には、一塩基変異が原因となっている疾患が多数存在します。塩基編集は、それらの遺伝性疾患の治療において画期的な治療法を提供できる可能性を秘めています。
バイオパレットでは、マイクロバイオーム治療を除いたヒト治療の分野は、バイオパレットの有する技術をBeam Therapeutics社へ独占的にライセンスアウトすることにより、同社をグローバル・パートナーとして事業展開を図っています。現在Beam Therapeutics社は、遺伝性の血液疾患である鎌状赤血球症やβサラセミアの新規治療法の実用化に向けた開発を推進しています。なお日本での開発については、両社がより密接に連携して事業展開を行います。Base editing that allows precise and accurate gene editing (Target-AID®) is expected to have applications in the field of human therapeutics. In principle, the use of base editing can make it possible to repair genes without gene disruption, and without even inserting DNA fragments. Many genetic diseases are caused by mutation of a single base. Base editing has the potential to provide groundbreaking therapeutics for the treatment of these genetic diseases.
By exclusively licensing out our technology to Beam Therapeutics for the field of human therapeutics excluding microbiome therapeutics, Bio Palette is collaborating with Beam Therapeutics as a global partner. Beam Therapeutics is currently developing novel treatments for sickle cell disease and beta-thalassemia, an inherited blood disorder, for commercialization. Both companies will coordinate closely when developing their businesses in Japan. -

-
農業(植物細胞が対象)
Agriculture (Targeting plant cells)
塩基編集を作物育種に利用することで、従来の遺伝子組換え技術で行われてきたように穀物に有用形質を付与して効率的な農業生産に寄与するほか、野菜や果物などにおいて特定の成分量を調整することで、栄養価の向上、アレルゲンの低減、保存性の改善など、消費者に直接的なメリットを提供する作物を創出することが期待されています。
特に、バイオパレットの技術であるTarget-G®による進化工学的な育種と、Target-AID®による精密かつ正確な点変異導入の組み合わせは、他社にはない効率的な植物育種を実現するための強力なツールとなります。The use of base editing in crop breeding will contribute to an efficient agricultural production by adding useful traits to grains, as has been done with conventional genetic modification techniques. Furthermore, creating fruits or vegetables that offer direct benefits to consumers, such as increased nutritional value, reduced allergens and improved shelf life are expected by adjusting the amount of certain ingredients.
In particular, a strong combination of breeding by evolutionary engineering using Target-G® and introduction of precise point mutations using Target-AID® will be a powerful tool for enabling efficient plant breeding. -

-
研究用ツール
Research Tools
塩基編集技術は、新たな研究用ツールの開発にも応用することが可能です。当社の技術(Target-AID®)を用いて開発された大腸菌コンピテントセルが、株式会社バイオダイナミクス研究所(販売代理店:フナコシ株式会社)より販売されています。
製品情報: https://www.funakoshi.co.jp/contents/68230Base editing technology can also be applied to the development of useful research tools. The E. coli competent cells developed with our technology Target-AID® are available from Funakoshi Co., Ltd., a sales agent of BioDynamics Laboratory, Inc.
Product Information: https://www.funakoshi.co.jp/contents/68230 -

Contact
バイオパレットへの各種お問い合わせおよび
パートナーシップのご相談はこちらからどうぞ。
For general inquiries or partnering requests,
get in touch with us from here.